What is Dumpy Level?
Dumpy level is commonly used leveling instrument to locate the points in same horizontal plane. It is also called as automatic level or builder’s level. Elevations of different points and distance between the points of same elevation can be determined by dumpy level.
The telescope is fixed to its supports in dumpy level and hence it cannot be rotated in vertical axis. It is invented by William Gravatt in 1832.

Components of Dumpy Level
Dumpy level consists the following parts or components
- Telescope
- Bubble tubes
- Compass
- Vertical spindle
- Tribrach screws
- Foot screws
- Leveling head
- Tripod
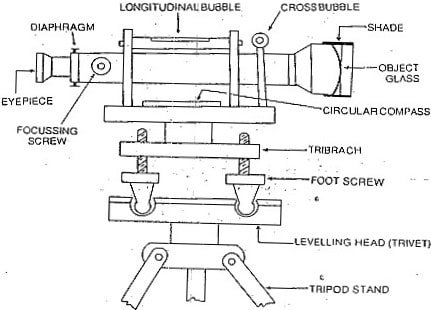
Fig: Components of a Dumpy Level
Telescope
Telescope is used to observe the distant object through line of sight provided by its arrangement. In general, the telescope is fixed to the vertical spindle of dumpy level so that it can be rotated along with vertical spindle.
Parts of Telescope in Dumpy Level
The important parts of telescope are as follows
- Eye piece
- Objective lens
- Diaphragm
- Focusing screw
- Ray shade
Eye piece
Eye piece is used by the observer’s eye to view the distant object. It contains magnifying glass which magnify the observing image and also the cross hairs of diaphragm. So, accurate reading can be obtained. Erecting eyepiece is used to view the normal image which is generally inverted by objective lens.
Objective lens
Objective lens are provided at the other end of the telescope. The objective lens consists of two parts, the front part consists convex type lens and the back part consists concave lens. So, the image obtained from the objective lens is always inverted.
Diaphragm
Diaphragm is provided in front of the eye piece. It contains cross hairs made of dark metal which are arranged in perfect perpendicular positions. These cross hairs are used by the eye piece to bisect the objective through objective lens.

Focusing screw
Focusing screw is used to adjust the focus if cross hairs and the image clarity. The magnification of eye piece is managed by this focusing screw.
Ray shade
Ray shade is used to prevent the objective lens from sunlight or any other light rays which may cause disturbance to the line of sight.
Bubble tubes
Bubble tubes are provided to check the level of the instrument. Two bubble tubes are provided in a dumpy level which are arranged perpendicular to each other on the top of the telescope. One tube is called as longitudinal bubble tube and another is called as cross bubble tube. The instrument is said to be in perfect position when both the bubbles of the tubes are at center or middle of the tube.
Compass
Compass is used to determine the magnetic bearing of line. In case of dumpy level, circular compass is provided just under the telescope. The compass contains a pointer in it and readings are marked inside it. The pointer is set to zero when it faces the north line from which the magnetic bearings are measured.
Vertical spindle
Vertical spindle is located at the center of the whole instrument. The telescope can be rotated in horizontal direction with respect to vertical spindle. The instrument is connected to the tripod stand using vertical spindle.
Tribrach
Tribrach plate is parallel to the leveling head or trivet. It is connected to trivet by leveling screws or foot screws which can adjust the tribrach plate. The horizontal level of the instrument can be achieved by adjusting this tribrach plate.

Foot screws
Foot screws are provided to regulate the tribrach position and hence the instrument can be leveled which is known by observing the bubble tube. The tribrach plates can be lowered or raised using foot screws. The position of tribrach is said to be correct when the bubble in bubble tube is at center.
Leveling head
Leveling head is also called as trivet. It contains two triangular shaped plates which are arranged parallel to each other. Three groves are provided at the three corners of the plates in which foot screws are supported.
Tripod
Tripod is used to support the whole leveling instrument on its top. It consists three legs which can be adjustable to required position. The legs are of same height and they may be solid or hollow. Steel shoes are provided at the bottom of each leg to hold the ground in a fixed position.

Procedure of Dumpy Level Surveying
The procedure of dumpy level surveying starts with some temporary adjustments which are:
- Setting up of instrument
- Leveling up
- Focusing
Setting up of Dumpy Level
The instrument is fixed to the tripod stand using clamp screws. Spread the tripod legs and position the instrument at convenient height. Firstly fix the two legs in the ground at a point and centering of bubble in the bubble tubes is done by adjusting third leg.
Leveling up
The leveling up of an instrument is done using foot screws or leveling screws. In this case, the telescope is arranged parallel to the any two leveling screws and the bubble in the tube is centered by turning both the screws either inwards or outwards.
When it is centered, then the telescope is turned 90o and the third screw is turned until the bubble come to center. Repeat the process until the bubble in the tube always stays at the middle in any position of telescope.
Focusing
Focusing is done by adjusting eye piece and focusing screw. Eye piece is adjusted until the cross hairs of diaphragm are clearly visible. To eliminate the parallax error, a white paper is used to obtain sharp vision of cross hairs.
Focusing screw is adjusted to view the clear image of the objective or staff. Focusing is said to be done when the cross hairs bisect the objective or staff with clear vision.
After completion the above temporary adjustments, now it’s time to take levels of required positions or points. The telescope is rotated towards the line of objective or staff and bisect it. The levels are noted at different points which values are decided from a known bench mark point in that area. The details are tabulated as below.
| Position observed | Level reading | HCR (higher cross hair reading) | LCR (lower cross hair reading) | (HCR-LCR) x 100 | Distance of point from instrument | Remarks / Error |
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | ||||||
| 3 |
Benefits of Dumpy Level Surveying
- Dumpy level is easy to use.
- Adjustments can be made as per the requirement on any type of ground.
- Level readings are very accurate in case of dumpy level.
- Optical power is high for dumpy level.
- Price of dumpy level is cheap when compared to other instruments.
Drawbacks of Dumpy Level Surveying
- It is limited to only horizontal angle measurement.
- The angles obtained by dumpy are not that accurate.